Despite the dominance of Google Chrome’s market share, there’s still more than a third of web usage worldwide that occurs on non-Chrome browsers. Given the complexity of supporting thirty years of web standards, it’s not surprising that the same web application can present divergent behavior across browsers. This makes the task of testing across browsers especially important for developers who want to ensure a consistent, working experience for all users.
Testing across browsers presents its own challenges. For instance, Google Chrome can work on operating systems with little or no exception, while Safari only works on Apple systems like macOS, iPadOS and iOS.
This article will discuss what cross-browser testing is, what Selenium Grid is, and how to set up a Selenium Grid for cross-browser testing. You’ll need a working knowledge of web development, testing, and CLI scripting to follow along with this article.
What is cross-browser testing
Testing is an essential part of the software development process. There are many different kinds of testing that can be performed, such as security testing, unit testing, compatibility testing, API testing, and accessibility testing. What we’ll be focusing on in this article is cross-browser testing.
Cross-browser testing assesses the compatibility of web applications and sites across different browsers. This can be accomplished manually, by executing the test scenarios across all desired browsers, but this is time-consuming and inefficient. Instead, cross-browser tests can be set up to run in a fully-automated way by utilizing tools that support creating automating tests and running them automatically across browsers. .
What is Selenium Grid
Selenium is an open source test automation tool that allows you to write test scripts in different programming languages to create automated functional tests. It supports several popular browsers, including Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, and operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Selenium is available in the following distributions as a testing framework:
- Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE): This extension is used by Firefox and Chrome developers to record and perform automated tests for web applications.
- Selenium WebDriver: WebDriver is an API that allows you to control browser operations and execute automated browser tests from the operating system level.
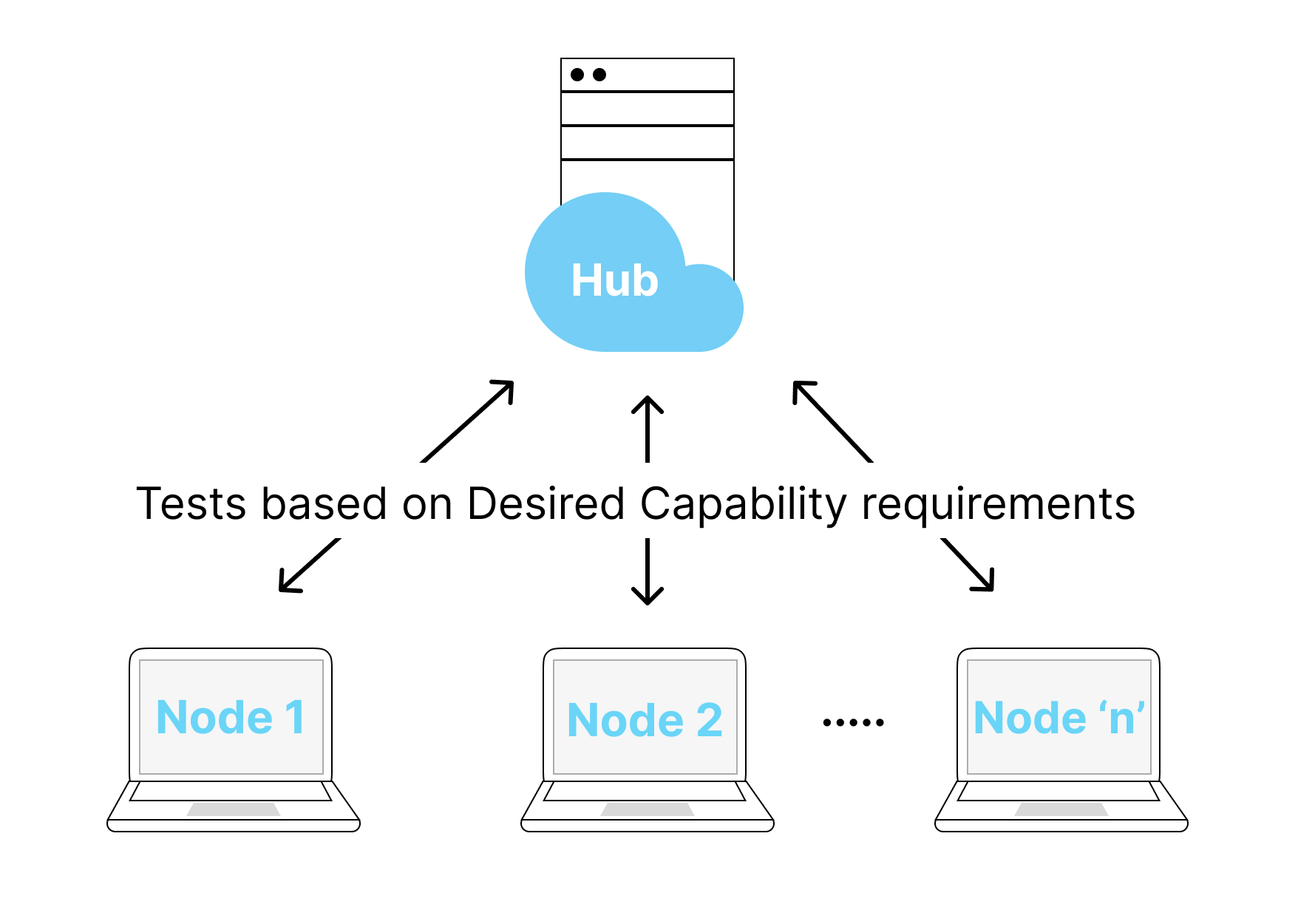
- Selenium Grid: Also called Selenium Server, Selenium Grid is comprised of a group of nodes connected to a single proxy server as the hub, Selenium Grid is used to run WebDriver scripts in parallel across the connected nodes.
Selenium Grid will be the emphasis of this article. Grid, unlike the other Selenium distributions, is best used for:
- Performing tests across different browsers, browser versions, and browsers running on different operating systems.
- Executing tests in a variety of runtime contexts.
- Optimizing testing on several levels, as this takes a long time.
Selenium Grid consists of two key sub-components:
-
Hubs/Servers: These are the core components of Selenium Grid infrastructure," and they load and distribute the tests to the relevant Nodes (clients) based on the desired capabilities (test execution request).
For example, imagine a Selenium Grid setup with two nodes configured: one for Safari 5.1.10 on MacOS, and another for Chrome 102 on Ubuntu. The hub is responsible for receiving a test execution request and routing it to the right node. If the “Desired Capabilities” requirement in the test execution request is “MacOS and Safari”, in this example it would be routed to the MacOS/Safari node.
-
Nodes/Clients: These are test environments connected to a hub to conduct tests. There are no limits to the number of nodes linked to a Hub, and the number of machines that can be on a Hub is unlimited.
Setting up Selenium Grid for cross-browser testing
To use Selenium Grid for cross-browser testing, we’ll need to set up a development environment that includes a hub and node.
Download and install the Selenium Server
Because the Selenium server is a jar file, make sure Java is installed and configured in the system PATH.
You can download the current version of the Selenium Server from the official website. There have been multiple version releases, so be sure to take note of the version you are using when following this guide.
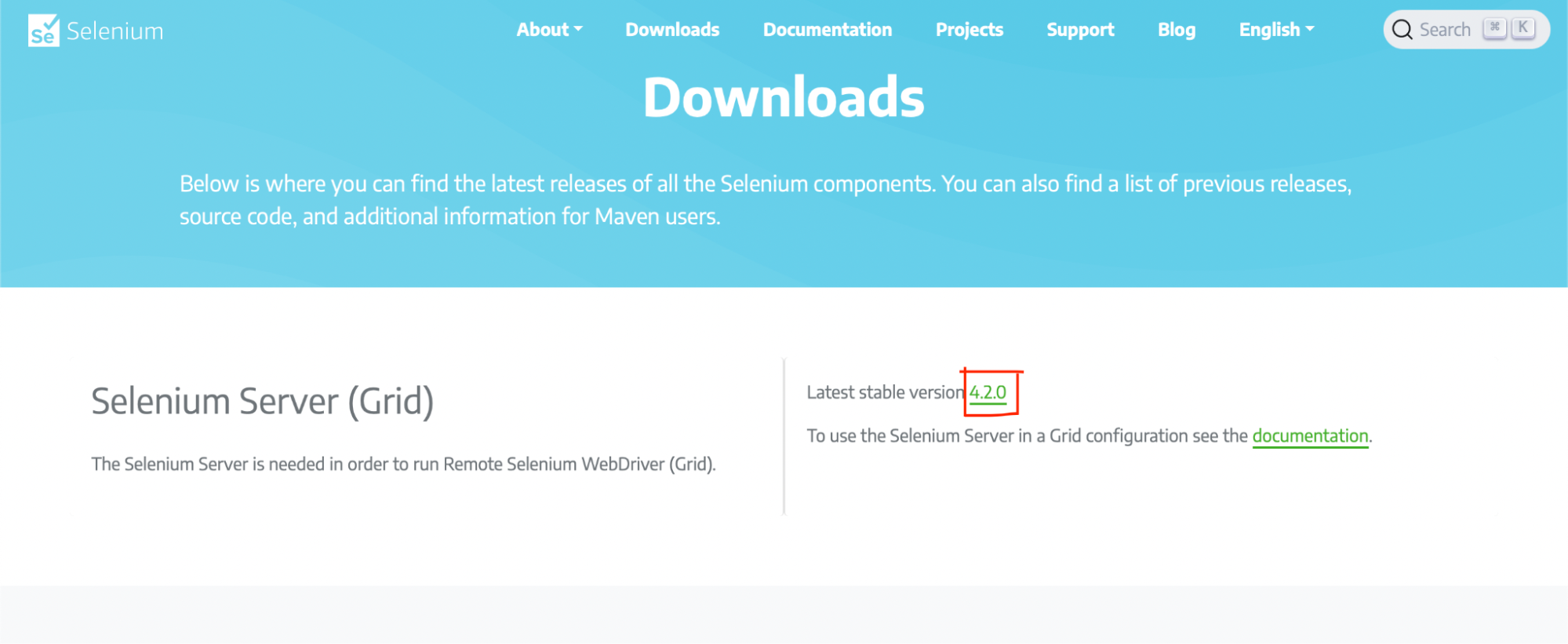
Starting Selenium Server
After you’ve downloaded the standalone file, start a terminal in the jar file’s directory and type the following command:
|
|
NOTE: Replace 4.2.0 with the current version you downloaded.
The command above will start the Selenium Grid Hub as a localhost server on port 4444, which you can alter by using the
-host parameter in the command above.
Accessing the Grid console
The Grid exposes the server’s numerous configuration details on the web page when you browse http://localhost:4444/grid/console.
On this page, you’ll see the link “View config” which will take you to a page with more information about the current hub’s settings.
Configuring a new node
With the steps we’ve done thus far, we’ve only managed to get one node up and running. We need to register a new port to build extra nodes. Therefore type the following command in the terminal:
|
|
The grid allows for five Chrome, five Firefox, and one Internet Explorer browser by default. To change this, add -browser “browserName=browser name>,version=browser version>,maxInstances=maximum instances of the browser>,platform=platform name>” to the command.
For example, on a Windows operating system, we may use the following command to allow only one instance of Firefox:
|
|
You’ll see that just one instance of Firefox is visible when you go to https://localhost:5555/grid/console.
The Grid hub and node machines should now be configured and ready for use. To execute test scripts on node machines, you can use an IDE like Eclipse or IntelliJ and create WebDriver code.
Selenium test scripts are distinct from other test framework script patterns, and the creators have provided guidelines detailing how to construct a functional, successful Selenium test script.
You can read the official documentation to learn more about writing test scripts for Selenium Grid nodes.
Conclusion
After reading this article, I hope you will understand the concept of cross-browser testing and start implementing it.
Understanding and utilizing Selenium Grid requires some expertise, but using it can improve the efficiency and speed of your tests and the scalability of your applications/products as long as you’re comfortable with building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure yourself.
Try Reflect: A modern cross-browser testing platform
Reflect is a no-code testing platform that lets you build and run tests across all popular browsers. Instead of building and maintaining your own infrastructure, using a cloud platform like Reflect allows you to get the benefits of automated cross-browser testing without the headache of maintaining an entire testing grid yourself.